What is online backup?
Online backup, also known as remote backup, is a method of offsite data storage in which files, folders, or the entire contents of a hard drive are regularly backed up on a remote server or computer with a network connection. A number of companies provide online backup services for subscribers whose computers are connected to the Internet, automatically copying selected files to backup storage at the service provider’s location. This is sometimes called Web-based backup.
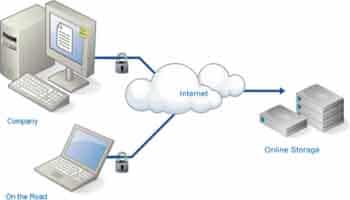
How online backup works?
Online backup systems are typically built around a client software program that runs on a schedule, typically once a day. This program collects, compresses, encrypts, and transfers the data to the remote backup service provider’s servers. Other types of product are also available in the market, such as remote continuous data protection (CDP).
Providers of this type of service frequently target specific market segments. High-end LAN-based backup systems may offer services such as near-realtime transaction-level replication or open file backups. Consumer online backup companies frequently have beta software offerings and/or free-trial backup services.
The rationale behind online backup is simple. By frequently (or continuously) backing up data on a remote hard drive, the risk of catastrophic data loss as a result of fire, theft, file corruption, or other disaster is practically eliminated. With a high-speed Internet connection and a Web browser interface, the remote files and folders appear as if they are stored on an external local hard drive. Encryption and password protection help to ensure privacy and security.
For the home and small business computer user, online backup services may be unaffordable if the intent is to totally back up a hard drive on a frequent basis. This problem can be mitigated by backing up only the most critical or often-changed files online, and using physical offsite backup methods for less important or infrequently changed files. For medium-sized and large enterprises or for particularly valuable data, the cost of online backup can prove to be a wise investment.
Advantages of online backup
Online backup has advantages over traditional backup methods:
- Perhaps the most important aspect of backing up is that backups are stored in a different location from the original data. Traditional backup requires manually taking the backup media offsite.
- Remote backup does not require user intervention. The user does not have to change tapes, label CDs or perform other manual steps.
- Unlimited data retention.
- Some remote backup services will work continuously, backing up files as they are changed.
- Most remote backup services will maintain a list of versions of your files.
- Most remote backup services will use a 128 – 448 bit encryption to send data over unsecured links (ie internet)
- A few remote backup services can reduce backup by only transmitting changed binary data bits
Disadvantages of online backup
Online backup has some disadvantages:
- Depending on the available network bandwidth, the restoration of data can be slow. Because data is stored offsite, the data must be recovered either via the Internet or via tape or disk shipped from the online backup service provider.
- Some backup service providers have no guarantee that stored data will be kept private – for example, from employees. As such, most recommend that files be encrypted before storing or automating this process.
- It is possible that a remote backup service provider could go out of business or be purchased, which may affect the accessibility of one’s data or the cost to continue using the service.
- If encryption password is lost, no more data recovery will be possible. However with managed services this should not be a problem.
- Residential broadband services often have monthly limits that preclude large backups. They are also usually asymmetric; the user-to-network link regularly used to store backups is much slower than the network-to-user link used only when data is restored.
