The native Windows Disk Management tool has "Shrink Volume" and "Extend Volume" functions to help change partition size without losing data (in most cases). However, many people have reported that the "Extend Volume" option is greyed out in Windows Server 2016 Disk Management. A typical example is when Extend Volume is disabled for the C drive after shrinking partitions D or E. This article explains all possible reasons why "Extend Volume" is grayed out in Windows Server 2016 Disk Management and how to fix this issue easily.

Why Extend Volume greyed out in Windows Server 2016:
There are 4 reasons why "Extend Volume" greyed out in Windows Server 2016 Disk Management:
- No adjacent unallocated space on the right
- Filesystem is not support.
- Different partition type on MBR disk
- 2TB restriction on MBR disk
I'll explain one by one.
① No adjacent unallocated space on the right
You can resize a partition but you cannot resize a physical disk, a 256GB physical hard drive cannot be increased to 512GB, Therefore, before extending a partition, you must shrink or delete another volume to get unallocated space on the same disk. By deleting a partition, all its disk space will be converted to "unallocated", but all files in it will be deleted. By shrinking a drive, only part of the free space will be converted to unallocated but you won't lose files in it.
If you did not shrink or delete other volume to get unallocated space, of course Extend Volume is grayed out in Server 2016 Disk Management.
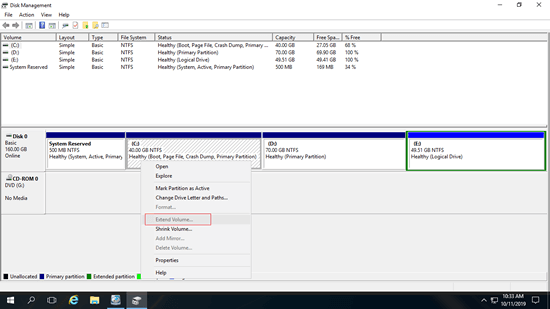
Many server administrators did shrink drive D/E before extending C: drive, but Extend Volume is still disabled in Windows Server 2016.
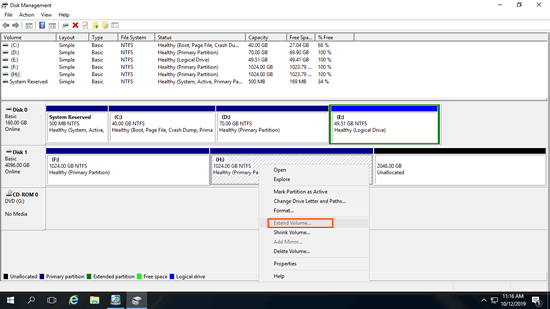
The "Shrink Volume" function can only create unallocated space on the right while shrinking a partition. The "Extend Volume" function can only combine unallocated space with the contiguous partition on the left. Since the C drive is nonadjacent and the E drive is on the right of the unallocated space, the "Extend Volume" option is disabled for both the C: and E: drives after shrinking the D drive. This is the most common reason why the "Extend Volume" option is greyed out in Server 2016 Disk Management.
② Filesystem is not supported
The "Extend Volume" function only supports extending NTFS and RAW (no file system) partitions. Therefore, FAT32 and any other types of partitions cannot be extended, even if there is adjacent unallocated space on the right.
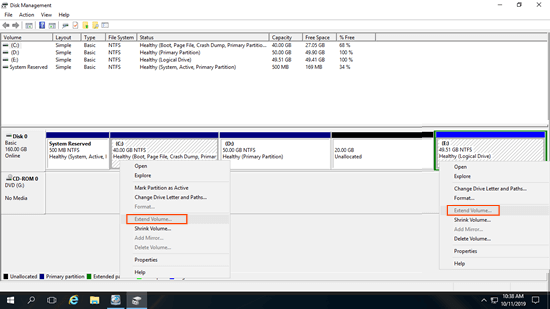
To show you this shortage, I formatted D: drive from NTFS to FAT32. As you see in the screenshot, although there's 20GB unallocated space behind D drive, "Extend Volume" is still disabled.
In most of Windows servers, system C drive is formatted with NTFS, so this issue is just common to data drives.
③ Different partition type on MBR disk
Because it doesn't work by shrinking a volume, some people are wondering whether it works by deleting partition instead. The answer is different on GPT and MBR disk.
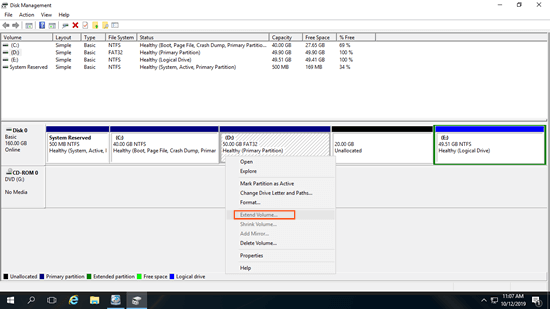
On GPT disk, all partitions are primary, but on MBR disk, there could be both primary and logical partition. If the type of partition that you want to delete and extend are different, Disk Management cannot extend partition even after deleting the contiguous volume.
As you see in the screenshot, Extend Volume is disabled for D: drive after deleting the right contiguous partition E.
This is because:
On MBR disk, "Free" space that deleted from a logical drive can't be extended to any primary partition. "Unallocated" space that deleted from primary partition can't be extended to any logical drive.
Note: this issue only exists in Disk Management, if you delete volume with NIUBI Partition Editor, you can combine unallocated space to either adjacent partition directly.
④ 2TB restriction on MBR disk
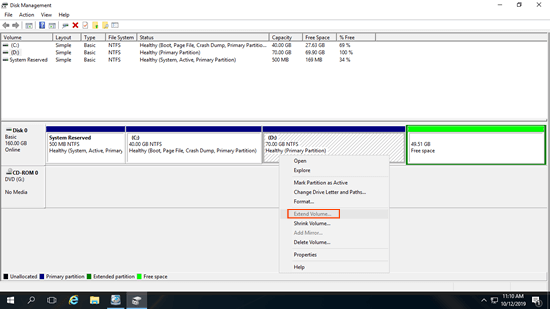
Nowadays, hard disks are much cheaper and larger. It is very common to use 4TB single disk or over 10TB RAID array. If you initialized a large disk or RAID as MBR, you can only use 2TB disk space in Disk Management.
As the screen shot shows, drive H is formatted with NTFS and there is adjacent contiguous unallocated space on the right, but Extend Volume is still grayed out.
To use full 2TB+ disk space and extend a partition larger than 2TB, you need to convert disk from MBR to GPT in advance.
What to do when Extend Volume is disabled in Server 2016
Open Disk Management and find out your server disk partition configuration. Follow the corresponding solution below according to your own disk partition structure. Each solution has a video guide.
Solution 1: Move unallocated space
Steps when Extend Volume greyed out in Server 2016 after shrinking D drive:
- Download NIUBI Partition Editor, right click D: drive and select "Resize/Move Volume", drag the middle of D drive to the right in the pop-up window. Then unallocated space will be moved to the left.
- Right click C: drive and select "Resize/Move Volume" again, drag the right border to the right to combine this unallocated space.
- Click "Apply" on top left to execute. (All operations before this step only work in virtual mode.)
If there's EFI, Recovery or other partition behind C drive, follow the same method to move these partition to the right.
Solution 2: Resize partition with NIUBI
To fix Extend Volume greyed out in Windows Server 2016 because of non-supported FAT32 partition or different partition type:
- Run NIUBI Partition Editor, right click the adjacent partition and select "Resize/Move Volume".
- Drag the border towards other side to combine unallocated space to either adjacent on the left or right.
- Click Apply on top left to execute.
Solution 3: Convert MBR disk to GPT
When you cannot extend a partition pass 2TB in Windows Server 2016, follow the steps below:
- Run NIUBI Partition Editor, right click front of this disk and select "Convert to GPT disk".
- Run "Resize/Move Volume" function and combine unallocated space to the partition(s) that you want to expand.
Take care of data while extending partitions in a server
Unlike read-only programs, partitioning software modifies the parameters of the associated disk, partition, and files. Therefore, there is a potential risk of system damage and data loss, especially when shrinking and moving partitions. Remember to back up in advance and use safe partition software.
Better than other tools, NIUBI Partition Editor has innovative technologies to protect system and data such as:
- Virtual Mode – All operations will be listed as pending for preview. Real disk partitions won’t be changed until you click “Apply” to confirm.
- Cancel-at-will – If you apply incorrect operations, it doesn’t matter; you can cancel the ongoing operations without damaging the partitions.
- 1-Second Rollback – If any error is detected while resizing the partition, it automatically reverts the server to its original status in a flash.
- Hot Clone – Clone the disk partition without interrupting the server. You can clone the system disk regularly and boot from the cloned disk immediately if the system disk fails.
NIUBI Partition Editor is 30% to 300% faster when shrinking, moving, and copying partitions because it has an advanced file-moving algorithm. In addition to helping fix the "Extend Volume" greyed-out issue in Windows Server 2016/2019/2022/2012/2008/2003, it also helps you merge, optimize, convert, hide, wipe partitions, scan for bad sectors, and much more.